

NEW YORK - A T-cell receptor (TCR) is a complex protein responsible for activating T-cells, an important part of the body’s immune response to antigens. TCRs are located on the surface of T-cells. Their purpose is to recognize fragments of antigens called peptides - short amino acid sequences on the surface of TCRs that bind to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules.
TCRs have two chains, TCR alpha and TCR beta. Each has complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) responsible for binding TCRs to antigenic peptides. Detecting the antigenic peptides bound to MHC molecules requires specific TCR sequences to be bound to these MHC molecules. Recent computational tools have proposed more efficient means of predicting epitopes - the parts of antigen molecules to which antibodies attach themselves - which is important for cancer immunotherapy. T-cell epitope prediction refers to the task of finding the shortest peptides within an antigen to stimulate CD4 or CD8 T cells. Figure 1 below shows peptide prediction in T-cells, with (a) showing a T-cell expressing CD4 and bound to an MHC molecule, while (b) shows T-cells expressing CD8 and bound to an MHC molecule.1
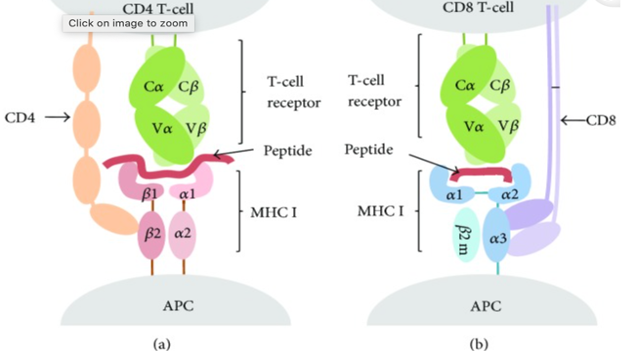
Figure 1: T-cells binding to MHC molecules
The topic of peptide drugs is interesting for many researchers, and in recent years various methods have been developed to find and predict the interactions of peptides. The importance of predicting those between peptides and ligands - molecules that bind to other, often larger ones - has led to the development of an array of computational methods in this field. There are two methods for protein-ligand interactions - sequence-b
The content herein is subject to copyright by The Yuan. All rights reserved. The content of the services is owned or licensed to The Yuan. Such content from The Yuan may be shared and reprinted but must clearly identify The Yuan as its original source. Content from a third-party copyright holder identified in the copyright notice contained in such third party’s content appearing in The Yuan must likewise be clearly labeled as such. Continue with Linkedin
Continue with Linkedin
 Continue with Google
Continue with Google











 1246 views
1246 views






