ONTARIO, CANADA - COVID-19 revealed the vulnerabilities of healthcare systems worldwide. Regardless of their levels of development, all countries had to grapple with a lack of preparedness in their existing strategies and policies - from highly imbalanced doctor/nurse to patient ratios and healthcare infrastructure or capacity, to overall inefficient budget allocations and utilization of healthcare across nations.
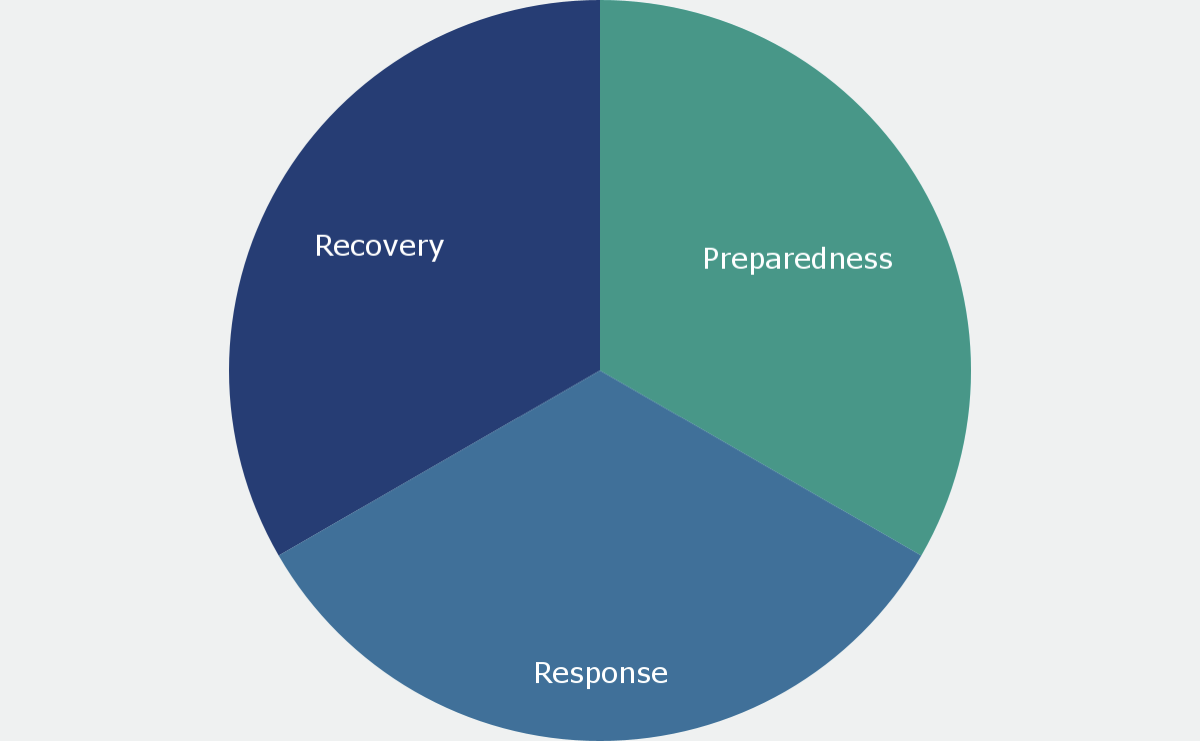
However, it also provided key lessons on how to efficiently manage a pandemic. The world witnessed how some countries in particular exemplified better pandemic management, commonly embracing technological trends like digitalization and artificial intelligence (AI) as winning tactics - or at the very least as crucial components. In areas where apprehension and resistance to adopting AI were more difficult to overcome, the pandemic proved an opportunity to demonstrate how AI enables human expertise, rather than threatening to replace it. With that context, one can examine how different countries enlisted AI's capabilities to implement pandemic management across the preparedness, response, and recovery phases.1
AI was critical in identifying the novel coronavirus well before the World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a pandemic. Leveraging its AI-powered platform, the Canadian health monitoring firm BlueDot flagged an outbreak of an unusual type of pneumonia in the city of Wuhan, China as early as December 2019, echoing the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome that had occurred over a decade earlier.2 This early alert was derived by a platform that synthesizes a diverse range of data - including news and ticket sales from over 4,000 airports - which are then verified by human experts. Thanks in part to BlueDot’s sounding of the alarm, the Chinese a
The content herein is subject to copyright by The Yuan. All rights reserved. The content of the services is owned or licensed to The Yuan. Such content from The Yuan may be shared and reprinted but must clearly identify The Yuan as its original source. Content from a third-party copyright holder identified in the copyright notice contained in such third party’s content appearing in The Yuan must likewise be clearly labeled as such. Continue with Linkedin
Continue with Linkedin
 Continue with Google
Continue with Google







 1504 views
1504 views