


NEW YORK - Cell morphology is an indicator of tissue function. When a disease is developing, the cell morphology changes, and this is the reason pathologists are interested in applying automatic methods of finding the relationships between the cell morphology and the disease state. This can be seen in some types of cancer, where the epithelial cells change their shape to convert to migratory phenotypes.
Pathologists currently do most of these analyses using the traditional methods of detecting cell types and disease. However, recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have motivated these experts to start extracting more information automatically. More specifically, applying machine learning (ML) tools to make an accurate model to find the associations among the morphological features with disease status has become of great interest to AI scientists.
Nowadays, with the rapid grow of image data from cells identification of cell types, knowledge extraction from data based on computer-assisted methods has become essential, not just something that is ‘nice to have.’ Cell images are captured with advanced microscopes, with each image containing white blood cells (WBC) and red blood cells (RBC). Basically, WBCs are the principal components in the human body’s immune system. WBCs can be segmented into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Figure 1 below shows an example of a cell image. There are various characteristics in each nucleus and cytoplasm based on density and shape - including areas, perimeters, Feret diameters, and more - which help to quantify each image.
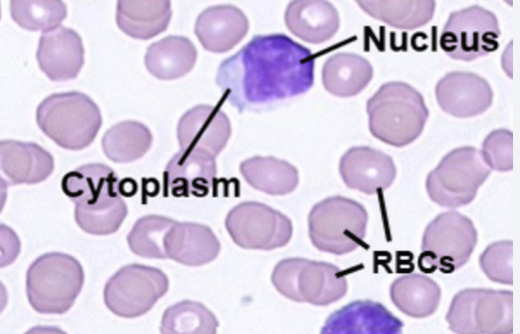
Fig. 1): An example of a cell image1
There are multiple WBC types that have differently shape
The content herein is subject to copyright by The Yuan. All rights reserved. The content of the services is owned or licensed to The Yuan. Such content from The Yuan may be shared and reprinted but must clearly identify The Yuan as its original source. Content from a third-party copyright holder identified in the copyright notice contained in such third party’s content appearing in The Yuan must likewise be clearly labeled as such. Continue with Linkedin
Continue with Linkedin
 Continue with Google
Continue with Google










 602 views
602 views






