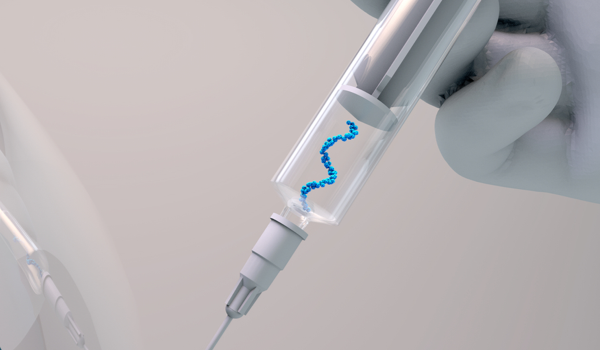
BOSTON - The discovery of the ribonucleic acid (RNA) vaccine and its use against COVID-19 represents a significant milestone in the field of virology and immunology as it has provided a new and more potent tool for providing protection against viral infections, with the potential to revolutionize the way the world approaches vaccination.
RNA vaccines are a type of vaccine that use RNA as their active ingredient, rather than deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). This sets them apart from traditional vaccines, which typically use inactivated or weakened forms of a virus itself to stimulate the body's immune response.
The idea of using RNA as a vaccine has been around for several decades, but it was not until recently that the technology needed to produce RNA vaccines at scale became available. The first RNA vaccine to be approved for use in humans was the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, which was developed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The science behind it all
The science behind RNA vaccines is based on the ability of RNA to directly activate the body's immune system. RNA is a molecule that is similar to DNA and is found in all living cells. RNA is involved in a number of important cellular processes, including the synthesis of proteins and the regulation of gene expression. When a person is exposed to a viral infection, his/her immune system produces antibodies to fight the virus. These antibodies are specific to the virus and help to neutralize it, preventing it from causing further harm.
RNA vaccines work by providing the body with a small piece of RNA that is derived from the virus. This RNA is taken up by antigen-presenting cells, which are a type of immune cell responsible for activating the body's immune response. Once inside the antigen-presenting cells, the RNA is translated into proteins, which are then presented o
The content herein is subject to copyright by The Yuan. All rights reserved. The content of the services is owned or licensed to The Yuan. Such content from The Yuan may be shared and reprinted but must clearly identify The Yuan as its original source. Content from a third-party copyright holder identified in the copyright notice contained in such third party’s content appearing in The Yuan must likewise be clearly labeled as such. Continue with Linkedin
Continue with Linkedin
 Continue with Google
Continue with Google








 970 views
970 views